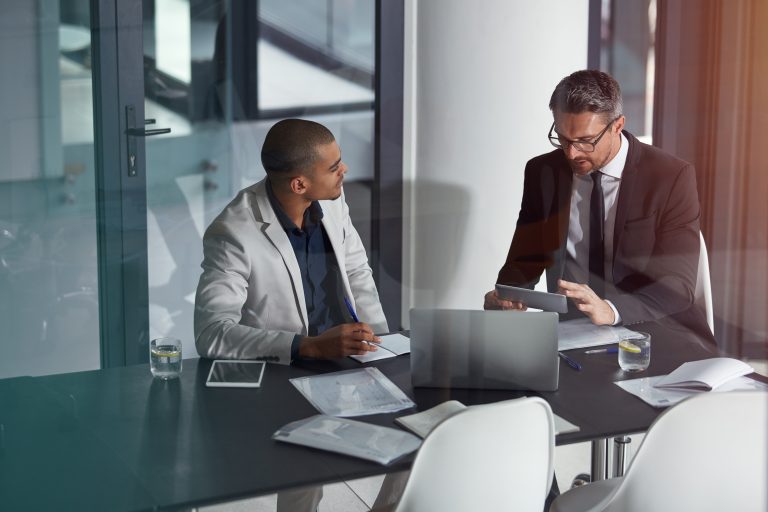
The UK-based embedded finance market is on a growth trajectory. It is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 19.5% from £6.47 billion in 2024 to £15.77 billion in 2029. This exponential growth has changed the fortunes of lenders to reach out to new channels through third-party channels. However, it also brings tough regulatory challenges to manage the risks and follow up with strict compliance standards.
As embedded lending models gain traction across fintechs, e-commerce platforms, and digital marketplaces, lenders must retain full visibility and control over risk. Embedding your products in third-party channels doesn’t dilute regulatory accountability; in fact, it intensifies the need for intelligent infrastructure and disciplined governance.
Regulatory Pressures Lenders Must Navigate in Embedded Lending
Understanding the regulatory landscape is crucial for lenders venturing into embedded distribution since they are under increased scrutiny by various regulatory bodies.
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) explains that lenders are held fully responsible for customer outcomes even if the loan is being provided under a third-party platform. The same applies to all phases of the lending cycle, ranging from the acquisition of initial customers to resolving complaints.
The Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) piles on the pressure by requiring operational resilience. When multiple third-party partners are in play, lenders must prove they can still keep key services running if something goes wrong in the chain.
With 94% of UK consumers citing security as their top concern when sharing personal data. Thus, lenders have to make sure that each embedded partner is GDPR and UK Data Protection Act compliant. Any breach of data or privacy taints the lending institution directly, irrespective of where it comes from in the value chain.
In practice, this means that partnering with third-party platforms does not dilute regulatory responsibility. Lenders must maintain full alignment with the FCA’s Consumer Duty, SYSC rules, and resilience requirements. Effective partnerships therefore depend on clear governance structures, strong oversight, and a shared commitment to safeguarding customers.
Trusted partners can make this process smoother. For instance, SaaS companies such as Pulse, which is also certified under the ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS), offer lenders a secure, compliant infrastructure that strengthens trust and mitigates regulatory risk in embedded finance collaborations.
Best Practices for Embedded Lending Partnerships
Due Diligence
Due diligence forms the basis of all other risk management activities in embedded lending. Lenders must check each third-party partner’s ability to meet regulatory standards and deliver fair customer outcomes before any integration starts. This check should include assessing the partner’s regulatory compliance history, financial stability, and technical abilities, with special attention to their understanding of UK-specific requirements.
Third-Party Oversight
All embedded partners must have systematic, risk-based evaluations and consistent compliance checks. This review should involve independent audit rights and requirements for the partners to provide key regulatory information in a timely manner. Regular monitoring helps detect emerging risks before they develop into regulatory breaches or customer detriment.
With 75% of financial institutions already implementing AI and another 10% with implementation on the cards within three years, regulatory frameworks need to allow for technological advancements.
Regulatory Reporting and Audit
Lenders must ensure timely and accurate reporting of incidents, compliance breaches, or operational disruptions involving third parties. This requires strong data collection systems that can aggregate information across several embedded channels without gaps or inconsistencies.
Audit trails must be maintained across all embedded lending activities to demonstrate compliance with regulatory expectations. These trails should include decisions made, risk evaluation, and remediation actions taken when issues arise.
Resilience Testing
Collaboration with critical partners in scenario-based operational resilience testing and business continuity planning is essential. These tests should simulate various disruption scenarios, including
- partner system failures,
- cybersecurity incidents, and
- market stress conditions.
It should reflect the interconnected nature of embedded finance ecosystems, where failures in one part of the value chain can cascade across multiple relationships.
Data Security and Privacy
GDPR and the Data Protection Act put data protection at the forefront of customer confidence. Partners must have regular system checks and hold security certifications, proving their dedication to securing customer data.
Given the security concerns, lenders must implement multiple layers of protection. It includes encryption of data in transit and at rest, robust access controls, and comprehensive audit logging of all data access activities.
Complaint and Remediation Processes
Transparent processes for resolving customer complaints and conducting root cause analyses must be maintained regardless of distribution channel. Customers must have clear, accessible channels for raising concerns, and lenders must maintain oversight of complaint resolution across all embedded partnerships.
Anti-Financial Crime Measures
All outsourced and third-party arrangements must establish anti-money laundering (AML), know-your-customer (KYC), and anti-fraud controls. Financial crime prevention must be consistent in all activities because criminals will exploit any weaknesses within embedded relationships.
Technology and API Governance
Data exchange and API integrations must be structured with robust security, access controls, and transaction traceability across all partners. Technical integration points represent critical vulnerabilities that require careful management through comprehensive governance frameworks.
API security measures should include authentication, authorisation, encryption, and rate limiting to prevent unauthorised access or system abuse.
Staying Competitive with the Right Tools and Mindset
As embedded lending reshapes the financial landscape, lenders must balance rapid expansion with disciplined risk management. The growth potential is undeniable, projected to reach over £15 billion by 2029; but so are the regulatory demands.
Meeting this challenge requires more than policy. It calls for smart technology to provide not just scalability, but measurable control, compliance, and resilience. Manual oversight can’t keep pace with the complexity of embedded distribution models.
That’s exactly where SaaS companies like Pulse excel. Pulse has developed a comprehensive suite of API-based lending solutions encompassed in Pulse’s Unified Lending Interface (ULI) that don’t just plug into ecosystems; they power them. Its end-to-end solution suite enables:
| Solutions | Description |
| Loan Origination System (LOS) | Automates and expedites the loan application and approval process for lenders |
| Loan Management System (LMS) | Manages and monitors loan repayments throughout the lending lifecycle |
| Einstein aiDEAL | It processes over 95% of deals in under a minute, offering an instant automated underwriting solution |
Together, these tools offer a unified lending interface that brings together security, traceability, and compliance, without sacrificing scale or speed. With Pulse’s ULI, lenders can confidently scale volumes and service a larger audience.
Speak with our experts to explore how Pulse can help you scale embedded lending securely and strategically. Book a demo today.