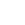Actionable insights driven by financial data intelligence
Designed to help businesses, lenders and accountants – our intuitive AI driven analytics platform will unlock the full potential of your financial data.
Book a demoOur Partners






Awards & Recognition





We connect you to your clients
Imagine giving your clients 24/7 access to a web-based portal that reveals the impact of every financial decision.
Pulse offers quick access to key business financial data, transforming it into actionable insights. This empowers you and your clients to make informed, successful decisions.
See all integrations30,000+
Open Banking Connections
4,000+
Open Accounting Connections
5,000+
Users









Presenting
Pulse is a powerful data analytics platform designed to provide a clear overview of key metrics and emerging trends, empowering users to unlock the full value of their business data.
With a wide array of user-friendly features, Pulse enables stakeholders at every level to make informed decisions, drive growth, and ensure sustainable success.

Instant insights across your portfolio
Access your portfolio of customers in your own web-based portal. Understand trend analysis and key metrics at a glance, helping you make more informed decisions with ease.
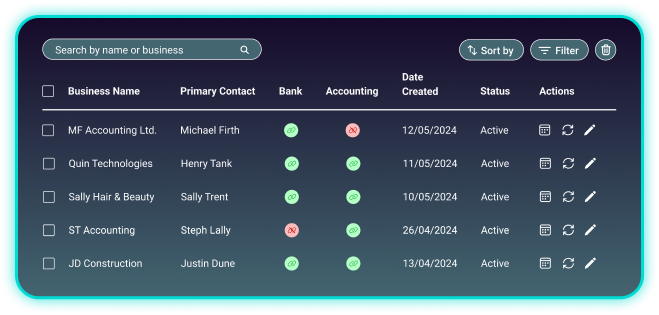

A data-driven tomorrow
Stay ahead with real-time alerts and prompts
‘Next Best Action’
Our AI model continuously analyses the data to identify key event triggers and prompt an action. Pulse keeps you informed so you can act quickly.
Automated alerts allow you to focus on strategic tasks while keeping track of critical updates.
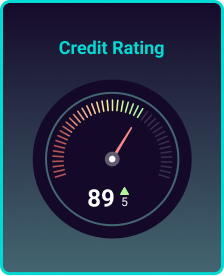
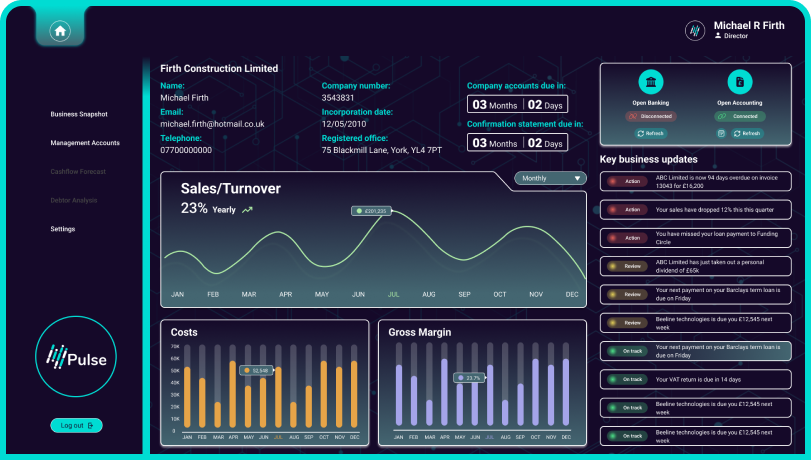
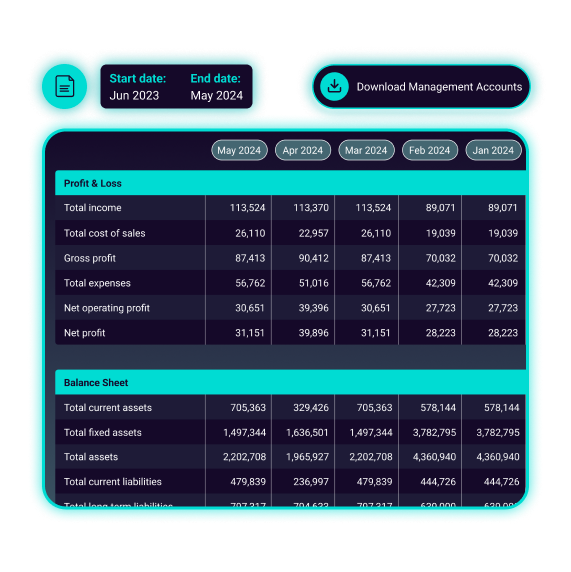
Monthly management accounts
View profit and loss accounts, and balance sheet data with ease. Pulse pulls data from accountancy packages, presenting it in a simple table format for quick understanding.
Connect for clarity
Frictionless integration for bank and accounting data
Easily connect your bank account and accounting software to Pulse, allowing you to generate a unified Pulse report that provides essential insights with minimal effort.
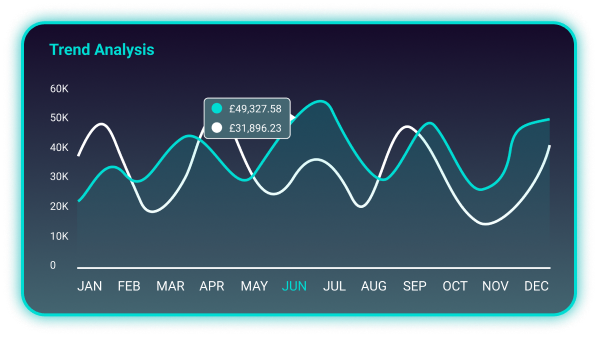
Visualise sales and turnover trends
Track turnover trends for your clients. Pulse helps you effortlessly identify high-performing months and those with lower sales.
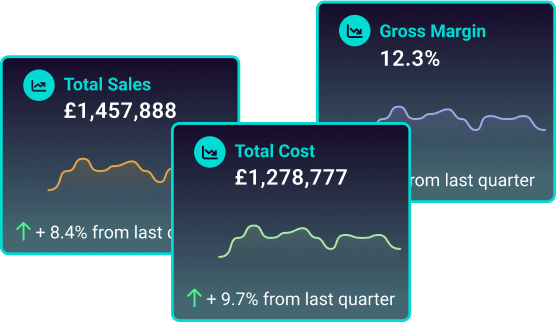
Cost and gross margin analysis
Understand how much your clients are spending and how much they’re making. Our graphs show 12 months of data, helping you spot trends and seasonal impacts on their businesses.

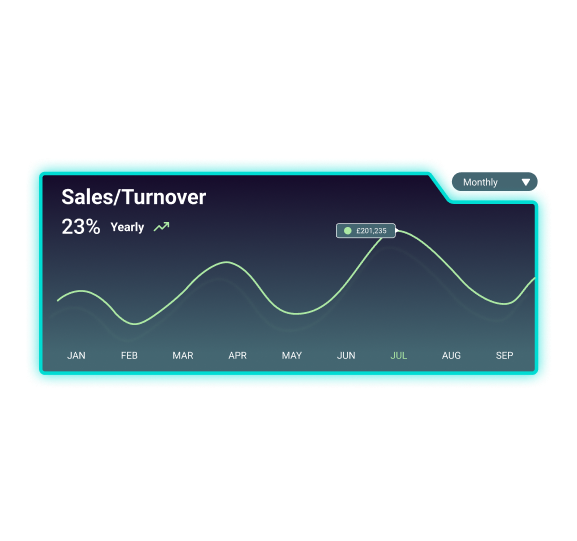
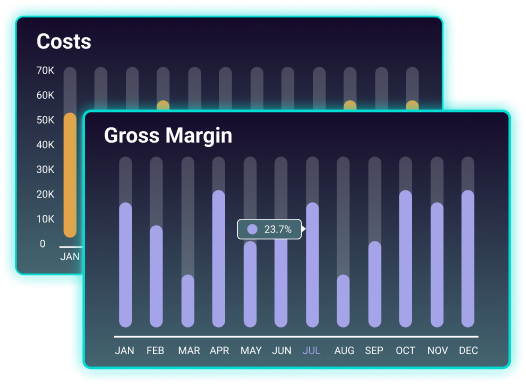

Assess financial health
Depict trend analysis
Analyse a range of metrics across your client’s businesses.
Our trend analysis graph shows you how sales and costs have evolved over the past year, helping you make informed decisions.
Focus on what matters most
Our snapshot page highlights select visuals from a range of areas, showing key growth or decline areas for your clients. Easily measure their business performance over the financial period.
Credit scores at your fingertips
Pulse provides access to your business credit score, empowering you to make informed decisions and develop strategic plans that improve financial health.
With this insight, you could unlock better financing options and drive long-term growth and stability.
Track goals and balances
Daily bank balance overview
Monitor your clients’ total bank balance daily, including accounts from multiple banks. Pulse ensures you’re always aware of their financial standing.
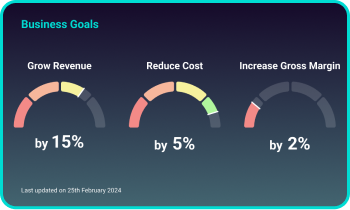
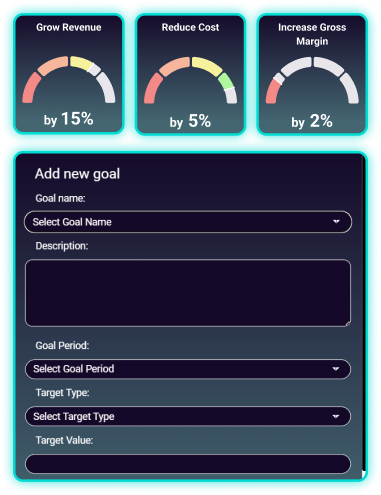
Set, track, and succeed
Help your clients plan for the future by setting goals
with Pulse.
Whether it’s increasing their revenue or cutting down on
costs, Pulse will keep you on track with timely
notifications.
Stay in control
The secret to mastering cash flow lies in having complete visibility of your incoming and outgoing finances, ensuring you keep your cashflow healthy and strong. Stay ahead by anticipating future cash needs and proactively planning for upcoming financial commitments.
Total Balance
£96,230.67

Safe and secure, as it should be
Built on trusted protocols and certified by Cyber Essentials Plus, we make it our priority to deliver class-leading security.
Leveraging the power of Microsoft Azure, Pulse ensures your data is managed on a secure, reliable, and scalable platform. We protect your financial information with comprehensive encryption, both at rest and in transit, and employ stringent security measures such as multi-factor authentication, geo-fencing, and IP restrictions to block unauthorised access.
Explore NowEvery device and user in the Pulse network benefits from enhanced protection through Microsoft Entra ID, guaranteeing the security of your digital identity at all turns.




Who we work with
At the heart of Pulse, we work with some of the market leading technology and service providers to deliver the best product capabilities and solutions for SMEs.
Whether you’re looking to streamline operations, enhance your marketing strategies, or explore new financial technologies, our marketplace is your gateway to a world of expertise.
Explore nowBe a part of our Partner Ecosystem
Join usWhy work with us?